Can Aluminum Be Used in Induction Cookware?
The introduction of induction cooking has transformed domestic cooking practices by offering enhanced temperature control and significantly expediting heating processes. However, issues arise concerning what materials are intrinsically suitable for induction cooking. Aluminum is often used in cookware because it is lightweight and has excellent thermal conductivity, but it creates a unique problem with induction compatibility. This article looks into whether aluminum can be incorporated into induction-compatible cookware, what solutions exist, and what factors to consider when selecting cookware designed to be compatible with induction ranges.
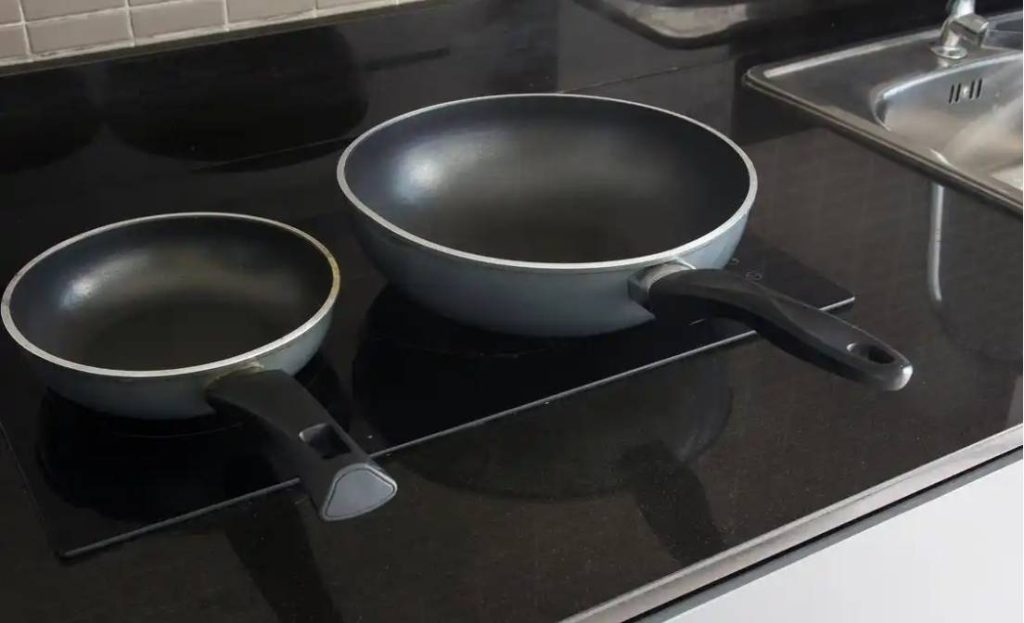

The Challenge of Aluminum on Induction
Aluminum is one of the most preferred materials used in cookware because of its conductivity and lightweight traits. On the other hand, its use with induction cooktops is problematic. In order to appreciate this cooking technology’s limitations, it is useful to analyze how induction cooking works and the reasons behind the use of certain materials over others.
Induction Cooking Concept
The principle of induction cooking makes use of magnetic fields to produce heat. Copper coils beneath the glass surface of an induction cooktop produce a magnetic field when current passes through them. This, in turn, produces electric currents within the cookware (eddy currents). These currents generate heat in the cooking vessel directly, rather than heating the cooktop first. Such a mechanism is very streamlined and has little waste heat.
The cookware must contain ferromagnetic materials, that is, materials which can interact with the magnet field. Cast iron and some stainless steels are good examples. Additionally, Cookware should not have rounded bottoms, as…
Why Pure Aluminum Doesn‘t Work
Pure aluminum is not ferromagnetic, meaning it does not respond to magnetic fields. While aluminum is an excellent conductor of heat and widely used in non-induction cookware, its non-magnetic nature makes it inherently incompatible with induction technology. As a result, an induction cooktop cannot generate heat in a pan made entirely of aluminum.
However, advancements in cookware design have found innovative ways to adapt aluminum for use on induction cooktops. In the next section, we will explore how manufacturers have successfully adapted aluminum to meet the demands of induction cooking.

Aluminum in Induction Cookware
Although pure aluminum cannot be used on induction cooktops, manufacturers have developed several methods to make it compatible.
Methods to Make Aluminum Work in Induction Cookware
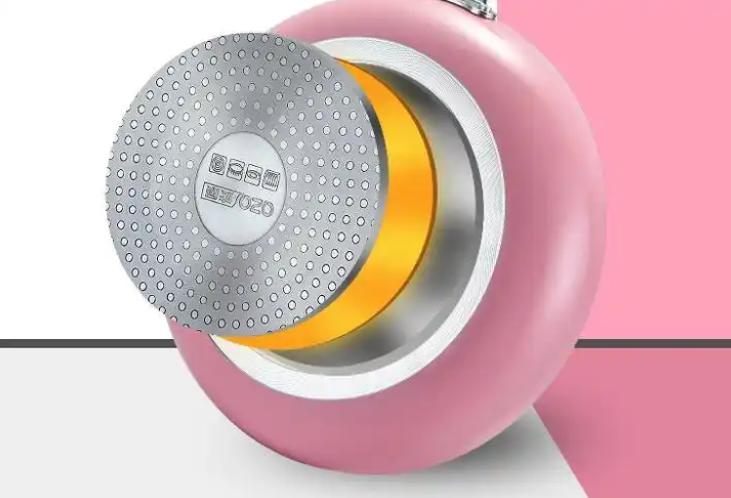
Magnetic Stainless Steel Base: One of the most common solutions is to attach a layer of magnetic stainless steel to the bottom of aluminum cookware. This layer interacts with the magnetic field, allowing the cookware to heat up, while the aluminum ensures even heat distribution across the cooking surface.
- Tri-Ply and Multi-Ply Construction: Aluminum is placed between two layers of stainless steel, making this design induction compatible due to the outer layer’s magnetism. The aluminum core ensures excellent heat conductivity, which helps in quick and uniform heating of the entire pan.
- Bonded or Cladded Aluminum: In mid-range cookware, it is quite common to find aluminum pans with a magnetic stainless steel disc bonded to their bottom. This approach works particularly well as a budget-friendly solution for making aluminum pans induction-compatible.
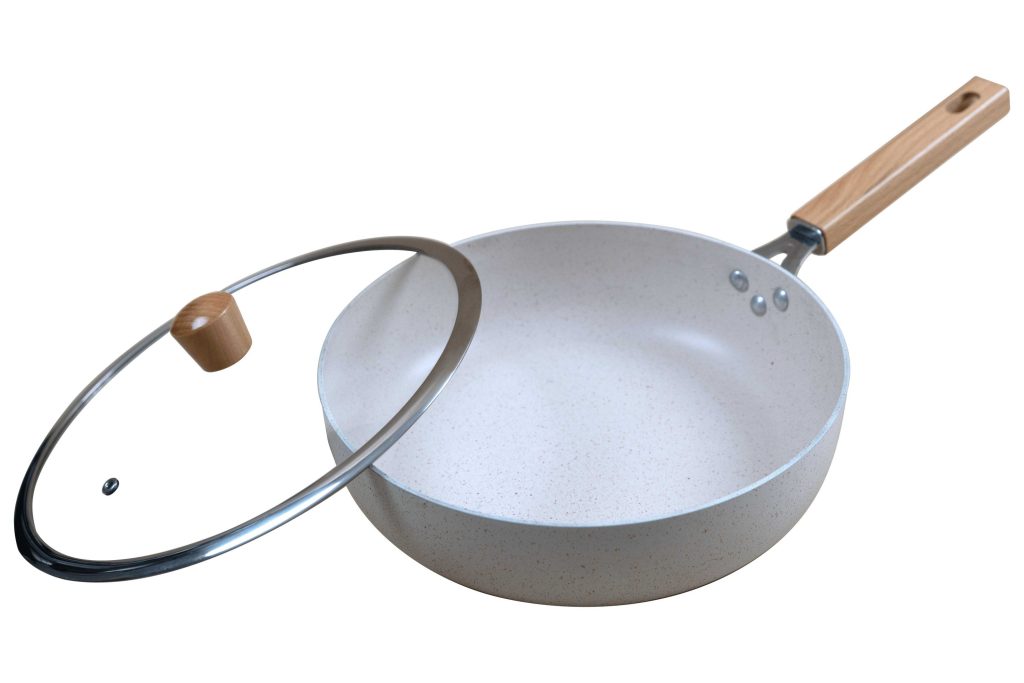
- Hard-Anodized Aluminum with Magnetic Base: This type of cookware combines the durability and non-stick advantages of hard-anodized aluminum with a magnetic stainless steel layer, allowing efficient use on induction cooktops while maintaining lightweight and sturdy features.
These innovative designs combine the best of both worlds: the superior heat conductivity of aluminum and the magnetic properties needed for induction cooking.

Advantages and Challenges
Advantages
- Lightweight: Aluminum cookware is significantly lighter than cast iron or solid stainless steel, making it easier to handle, especially for large pots and pans.
- Excellent Heat Conductivity: Aluminum heats up quickly and distributes heat evenly, preventing hot spots and ensuring consistent cooking results.
- Cost-Effective: Aluminum cookware, even with magnetic adaptations, is generally more affordable than high-end stainless steel or copper cookware.
- Versatility: Induction-compatible aluminum cookware often works on all types of stovetops, making it a flexible choice for various cooking environments.
Challenges
- Durability Concerns: The bonded or cladded magnetic layer may wear out or delaminate over time, especially with heavy use or improper care.
- Performance Differences: While aluminum is an excellent heat conductor, the magnetic layer’s effectiveness may not match the performance of solid ferromagnetic cookware.
- Verification Required: Not all aluminum cookware is induction-compatible. Buyers must ensure the cookware is explicitly labeled as suitable for induction use.
Despite these challenges, the benefits of combining aluminum with magnetic materials make it a practical choice for many households.
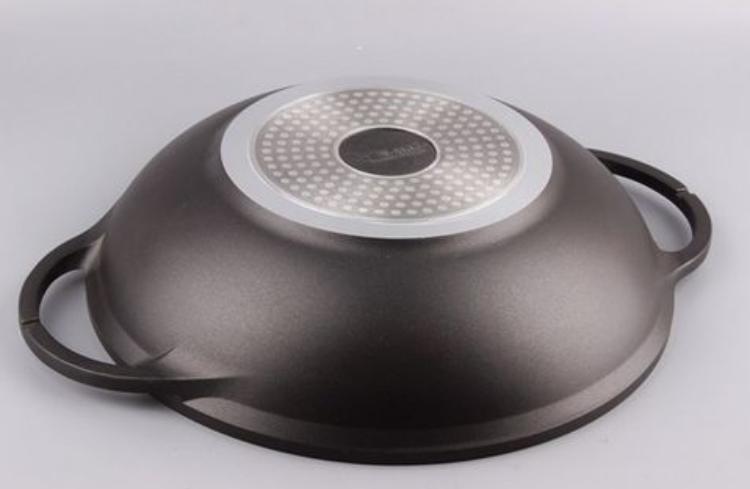

Choosing Induction-Compatible Cookware
When shopping for pots and pans for an induction cooktop, pay attention to the following:
- Induction Symbols: Many manufacturers have labels that signify the cookware as induction compatible.
- “Induction Ready” Labels: Mostly used in advanced modern cookware.
- Bottom Construction: Check the cookware’s bottom. It needs to have a level and usually a magnetized surface in order for it to be induction-compatible.
Familiarizing yourself with the problems and innovative approaches allows you to confidently select aluminum cookware for your induction cooktop as well as enjoy its benefits.
For any aluminum cookware, please feel free to contact us.
Related Products