5 Factors That Affect the Performance of Coated Aluminum Disks
In modern society, coated aluminum disks have a wide range of uses, from data storage and kitchenware, to automotive and aerospace applications. The coating applied to these disks not only enhances their appearance but also provides necessary resistance to corrosion, wear, and environmental damage. Their performance is affected by many factors. Understanding these factors is crucial for optimizing their design, manufacturing, and operation. Here we’ll explore the key factors that influence the performance of coated aluminum disks, covering aspects from coating material to environmental and operational impacts.

Factor 1: Coating Material and Thickness
The coating applied to aluminum disks is crucial in determining their functionality and performance. Coatings serve multiple purposes: they enhance corrosion resistance, improve wear resistance, increase thermal stability, and even improve aesthetic appeal. The choice of coating material and its thickness play a significant role in how well the disk will perform under different conditions.
Coating Material
Coating materials can range from anodized layers to powder coatings, ceramic coatings, and even specialized coatings for specific industries. Each coating type has distinct benefits:
- Anodized Coatings: Common in aerospace and automotive applications, anodized coatings provide excellent corrosion resistance and wear resistance. The anodizing process also increases the thickness of the natural oxide layer on aluminum, improving its hardness.
- Powder Coatings: Popular in industries where aesthetics are important, powder coatings offer both decorative appeal and functional benefits, such as resistance to scratching, fading, and weathering. They also provide good protection against corrosion.
- Ceramic and Specialty Coatings: These coatings are typically used in high-performance applications, such as in the automotive industry for heat resistance. Ceramic coatings can withstand high temperatures and protect against thermal expansion and contraction, enhancing the disk’s stability.
Coating Thickness
The thickness of the coating significantly impacts the durability and protection it offers. Thicker coatings generally provide better resistance to wear, corrosion, and damage. However, thicker coatings can also add weight, affect the disk’s dimensional tolerance, and impact its flexibility. In applications where precise tolerances are critical, thinner coatings may be preferred to maintain tight manufacturing specifications. For example, in electronics, where the disk must fit precisely into circuits, thinner coatings are usually chosen. In contrast, for heavy-duty industrial applications, thicker coatings are preferred to enhance performance under harsh conditions.
Choosing the right coating material and thickness is essential for maximizing the performance of coated aluminum disks. The material type determines the protective and aesthetic qualities, while the thickness directly affects the durability and wear resistance. Careful selection based on application requirements ensures optimal performance and longevity.

Aluminium Circle
Factor 2: Aluminum Quality
The quality of the aluminum substrate used in manufacturing disks is another key factor that influences the overall performance of coated aluminum disks. Aluminum’s composition, purity, and surface preparation are all critical considerations when evaluating substrate quality.
Aluminum Composition and Purity
Aluminum is available in various grades, with different purity levels. High-purity aluminum tends to have fewer impurities, leading to better performance when coated. The presence of impurities can weaken the bond between the coating and the aluminum surface, which may lead to premature peeling, corrosion, or failure of the coating over time. High-purity aluminum is especially important in industries like electronics, where precision and durability are essential.
Surface Preparation
Before applying the coating, the aluminum surface must be thoroughly prepared to ensure proper adhesion. Surface preparation methods include cleaning, etching, and priming the aluminum to remove oils, dirt, and oxidation. Proper surface preparation also helps to increase the surface area for better coating adherence. If the aluminum surface is not adequately prepared, it can lead to poor adhesion, resulting in coatings that can peel or flake off during use.
Structural Integrity
The physical properties of the aluminum, such as its strength, flexibility, and resistance to stress, also influence how well the coated disk performs. High-quality aluminum with uniform grain structure will allow the coating to perform as expected under mechanical loads and temperature fluctuations. Poor-quality aluminum with defects can lead to uneven coating application or failure of the disk under stress.
The quality of the aluminum substrate is foundational to the performance of coated aluminum disks. High-purity aluminum, combined with effective surface preparation, ensures strong adhesion of the coating and enhances the disk’s durability. The structural integrity of the aluminum also determines how well the disk can withstand operational and environmental stresses.
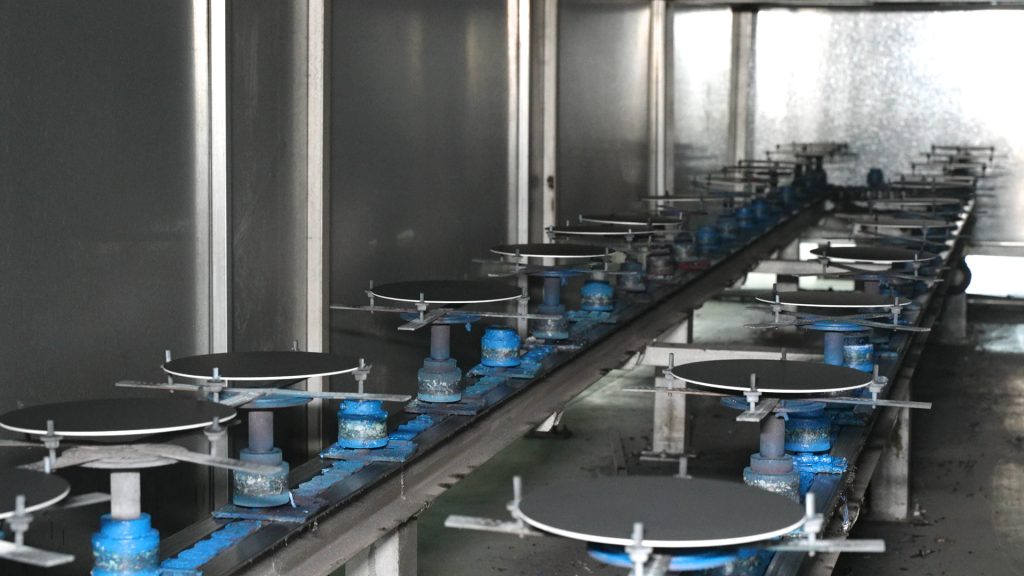

Factor 3: Manufacturing Process
The manufacturing process plays a pivotal role in determining the final performance of coated aluminum disks. From the application of the coating to the curing process, every step of the manufacturing process influences the disk’s overall quality, appearance, and functionality.
Pretreatment process factors
- Degreasing: If there is grease on the surface of the aluminum disk, it will seriously affect the adhesion of the coating. Grease will form an isolation layer between the coating and the substrate, preventing the effective bonding of the coating and the substrate. Incomplete degreasing may also cause defects such as shrinkage holes in the coating. During the degreasing process, parameters such as the type, concentration, treatment temperature and time of the degreasing agent need to be strictly controlled.
- Pickling and alkali washing: Pickling can remove the oxide film on the surface of the aluminum disk and activate the surface of the substrate, which is beneficial to improve the adhesion of the coating. However, excessive pickling may corrode the aluminum disk substrate and reduce its mechanical properties. Alkali washing can also remove surface dirt and oxide film. However, if the concentration of the alkali solution and the treatment time are not properly controlled, it will also damage the aluminum disk and may affect the quality of subsequent coatings.
- Surface activation treatment: Using chemical or physical methods to activate the surface of the aluminum disk can increase the surface energy and enhance the bonding between the coating and the substrate. For example, plasma treatment can introduce active groups on the surface of the aluminum disk to improve the adhesion of the coating. If the activation treatment is not done properly, the expected effect may not be achieved.
Coating process factors
- Spraying method
Using different spraying methods, such as air spraying, electrostatic spraying, etc., will affect the uniformity and quality of the coating. Electrostatic spraying can make the paint particles better adsorbed on the surface of the aluminum disk, improve the powder coating rate and the uniformity of the coating.
Parameters such as the spray gun distance, spray angle and spray gun movement speed during the spraying process also have an important impact on the coating quality. For example, if the spray gun is too far away, the speed of the paint particles will decrease when they reach the surface of the aluminum disk, and the coating adhesion will become poor; improper spraying angles may make some parts unable to be sprayed evenly.
- Curing process
Curing temperature and curing time are key parameters of the curing process. If the curing temperature is too low or the curing time is too short, the coating may not be fully cured, resulting in problems such as insufficient hardness and poor wear resistance of the coating.
Too fast a curing speed may cause stress inside the coating and cause cracking. Moreover, factors such as ambient humidity during the curing process will also affect the curing quality of the coating.
The manufacturing process, from coating application to curing, directly influences the performance of coated aluminum disks. The choice of coating technique, the precision of the coating application, and post-processing treatments can significantly impact the final product.

Factor 4: Environmental Factors
Environmental conditions can have a profound impact on the performance and longevity of coated aluminum disks. Exposure to temperature fluctuations, moisture, chemicals, and UV radiation can degrade both the aluminum and its coating.
- Temperature Fluctuations: Thermal expansion and contraction can cause coatings to crack, peel, or lose adhesion if they are not designed to handle temperature extremes. In applications where aluminum disks are exposed to high temperatures, such as in the automotive or aerospace industries, coatings with high thermal stability, like ceramic or heat-resistant powder coatings, are often required. Conversely, in cold environments, coatings need to remain flexible to prevent cracking under stress.
- Chemical Exposure: Exposure to corrosive chemicals, oils, or solvents can degrade the coating and the aluminum substrate. For example, coatings used in chemical processing or marine environments must offer excellent chemical resistance to prevent corrosion. Specialized coatings, such as epoxy or polyurethane, are often selected for their chemical resistance properties.
- UV Radiation: Outdoor exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation can cause coatings to fade, chalk, or degrade over time. This is particularly important in industries like construction or consumer products, where aesthetic and structural integrity are critical. UV-resistant coatings can mitigate this issue and prolong the lifespan of the aluminum disk in outdoor environments.
Environmental factors, including temperature fluctuations, chemical exposure, and UV radiation, significantly impact the performance of coated aluminum disks. Choosing coatings that are specifically formulated to handle these environmental stresses ensures that the disks maintain their performance and appearance in challenging conditions.
Factor 5: Operational Factors
In addition to environmental influences, the operational conditions under which a coated aluminum disk is used can also affect its performance. Factors such as mechanical stress, wear, and exposure to chemicals or heat must be taken into account during the selection and design process.
- Mechanical Stress: Coated aluminum disks used in high-stress applications, such as in machinery or transportation, must withstand forces like bending, twisting, and impact. Coatings that are flexible yet durable can help absorb and distribute stress, reducing the likelihood of cracking.
- Abrasion Resistance: For disks exposed to repetitive friction or contact with other materials, abrasion-resistant coatings provide protection against surface wear. This is critical in industrial applications where surfaces are frequently subjected to sliding or impact.
- Chemical Exposure: Operational exposure to chemicals, oils, or solvents can weaken certain coatings, reducing performance. Selecting a coating with high chemical resistance is essential for applications in chemically aggressive environments.
The performance of coated aluminum disks is influenced by a combination of factors, including the coating material and thickness, aluminum quality, manufacturing processes, environmental conditions, and operational factors. Each of these aspects plays a crucial role in determining how well the disk will perform under various conditions. Whether you are a manufacturer, a user or the brand owner, please carefully selecting the appropriate materials, processes, and coatings based on specific application requirements. If you are looking for a aluminum disk manufacturer, please feel free to contact us.